Constant Economies of Scale
In that case producers have an incentive to increase the level of production to improve profitability. This is the idea behind warehouse stores like Costco or Walmart.

Economies Of Scale How To Scale The Right Way
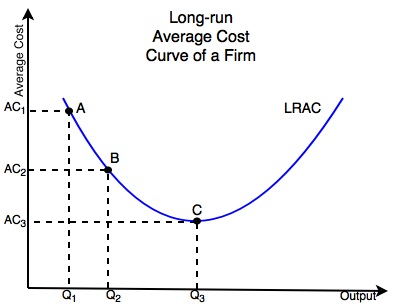
Figure 2 illustrates the idea of economies of scale showing the average cost of producing an alarm.

. Each single input however yields decreasing partial returns to scale ie. That means larger quantities can be produced at a lower average unit cost than smaller quantities. The more one increases the input of one single factor while leaving the other inputs constant the less is this factors marginal.
Economies of scale in production means that production at a larger scale more output can be achieved at a lower cost ie with economies or savings. The more one increases the input of one single factor while leaving the other inputs constant the less is this factors marginal return. Economies of scale refers to the situation where as the quantity of output goes up the cost per unit goes down.
A simple way to formalize this is to assume that the unit labor requirement in the production of a good is a function of the level of output produced. Labour and capital to exactly double the output produced. Goolsbee Levitt Syverson 2016 Microeconomics Worth Publishers.
As production volumes rise the total costs are spread out over the increased number. In Figure 61 Unit-Labor Requirement with Economies of. Economies of scale are distinguished into real economies and strictly pecuniary economies of scale.
1 The total cost of production divided over this larger number of units leads to a reduction in the average total cost per unit for example by making. Constant economies of scale. 2 Determinants of economies of scale 21 Physical and engineering basis.
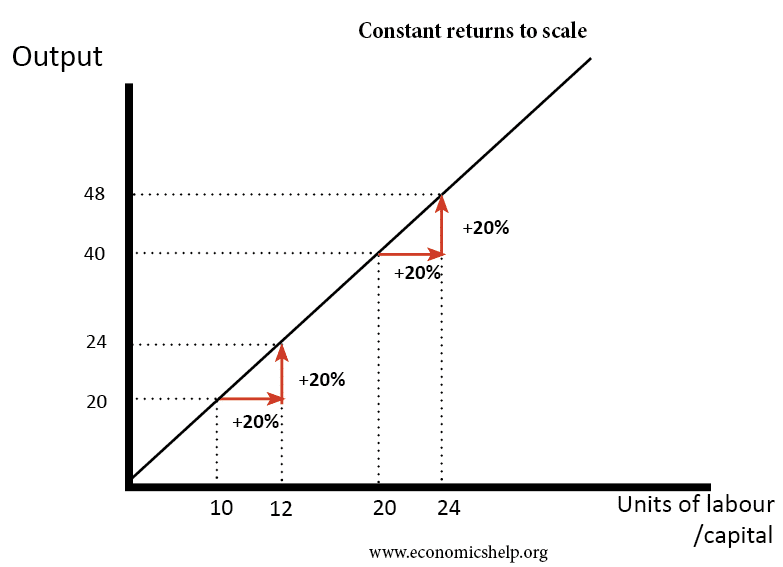
Means that it needs the double amount of all production factor inputs ie. Means that it needs the double amount of all production factor inputs ie. Economies of scale often occur because higher levels of production.
Returns to scale are long-run measurements. Labour and capital to exactly double the output produced. A larger factory can produce at a lower average cost than a smaller factory.
When a firm increases its production level the average cost per unit reduces. Even at such a level the company can experience economies of scale through bulk buying which results in decreased average cost. The economies of scale are cost benefits received by a firm through large-scale production.
Total cost rises at the same rate as output rises. Economies of scale are when a company lowers the per-unit cost of production while increasing production volume. Each single input however yields decreasing partial returns to scale ie.
This is the idea behind warehouse stores like Costco or Walmart. Define Constant economies of scale. Hence the economy of scale is achieved as a result of spreading costs over a large number of units.
Economies of increased dimension 22 Economies in holding stocks and reserves 23 Transaction economies 24 Economies deriving from the balancing of production capacity 25 Economies resulting from the division of labour and the use of superior techniques. The savings come from spreading the cost of production over a larger number of units. Economies of scale refers to the situation where as the quantity of output goes up the cost per unit goes down.
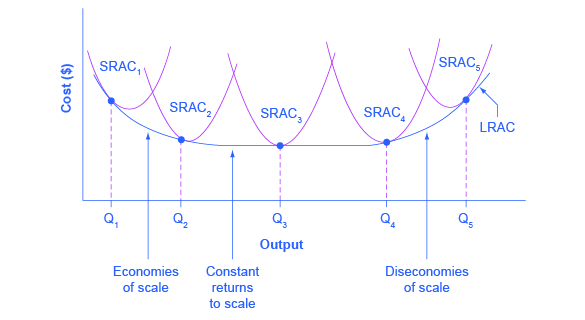
Economies of scale occur when the long-run average cost falls as the quantity of output increases. Many translated example sentences containing constant economies of scale German-English dictionary and search engine for German translations. A constant return of scale is an economic condition where a companys inputs like capital and labor increase at the same rate as their outputs or value of their goods.
Pecuniary economies are economies realized from paying lower prices for the factors used in the production and distribution of the product due to. Long run or long term refers to a period of a time within a company when their production factors are variable. There is an inverse relationship between quantity produced cost per unit.
Economies of Scale Definition Economies of scale is the concept suggesting that a business receives an advantage in cost per product produced as its output of the product increases. A larger factory can produce at a lower average cost than a smaller factory. Economies of scale means that production gets cheaper when more units are produced up to a certain point.
When an increase in inputs such as labor increases the production output in the same proportion a company is said to achieve constant returns to scale. Constant returns to scale. Economies of scale are cost advantages reaped by companies when production becomes efficient.
Hence it can increase the level of production and yet. Define Constant economies of scale. Companies can achieve economies of scale by increasing production and lowering costs.
Economies Of Scale Energy Education
Constant Returns To Scale Economics Help
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/MinimumEfficientScaleMES2-c9372fffba0a4a1ab4ab0175600afdb6.png)
Minimum Efficient Scale Mes Definition
Economies Of Scale Microeconomics

Economies Of Scale How To Scale The Right Way

2022 Cfa Level I Exam Cfa Study Preparation
0 Response to "Constant Economies of Scale"
Post a Comment